News
Aleksi Kurkela joins the EPJ Scientific Advisory Committee (SAC)
- Details
- Published on 05 December 2024

The Scientific Advisory Committee of EPJ is delighted to welcome Professor Aleksi Kurkela, as the new representative for the Norwegian Physical Society.
Aleksi Kurkela is an associate professor at the University of Stavanger, specializing in the intersection of high-energy nuclear and particle physics. His research focuses on the interdisciplinary connections between heavy-ion collisions and the physics of neutron stars.
EPJ Web of Conferences Highlight – 11th EPS-QEOD Europhoton Conference on Solid-State, Fibre, and Waveguide Coherent Light Sources (EUROPHOTON 2024)
- Details
- Published on 03 December 2024

The 11th EPS-QEOD Europhoton Conference took place in Vilnius, Lithuania, from August 25 to August 30, 2024.
Since its inception, the EPS-QEOD Europhoton Conference has become a pivotal event, showcasing the latest advancements in solid-state lasers, fiber and waveguide light sources. This 11th edition brought together leading experts, students, and industry professionals from around the world.
EPJ Web of Conferences Highlight – EOSAM 2024: EOS Annual Meeting
- Details
- Published on 03 December 2024

A Vibrant Gathering of Minds in Naples
The European Optical Society Annual Meeting (EOSAM) 2024 was held in Naples, Italy, September 9-13, at the CESTEV facilities of the University of Naples Federico II. This year's event was organized in close collaboration with the Italian Society for Optics and Photonics (SIOF), the Italian branch of the European Optical Society (EOS).
Silvia Masciocchi joins the EPJ Scientific Advisory Committee (SAC)
- Details
- Published on 21 November 2024

The Scientific Advisory Committee of EPJ is delighted to welcome Professor Silvia Masciocchi, as the new representative for the German Physical Society.
Silvia Masciocchi is a professor of physics at Heidelberg University and the head of the ALICE department at GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy Ion Research in Darmstadt, Germany. Her research focuses on exploring strongly interacting matter under extreme conditions, such as those created in ultra-relativistic heavy-ion collisions. These phenomena are studied in ALICE, one of the four major experiments at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN. Additionally, she is actively engaged in research and development (R&D) of advanced particle detection technologies, with a particular emphasis on semiconductor pixel sensors designed for high-precision position measurements.
EPJ B Highlight - Characterising shifts in Sicily’s seasonal rainfall
- Details
- Published on 19 November 2024

Over the past decade, rainfall patterns on Sicily have shifted from a 4- to a 2-season cycle, reflecting similar shifts taking place worldwide.
Around the world, man-made climate change is increasing both the frequency and severity of extreme weather events. Seasonal patterns in rainfall are an especially important indicator of these changes: while a lack of rain can lead to more severe droughts, an excess can trigger catastrophic events such as landslides and flash flooding. To better understand the impact of these risks, it is vital for researchers to characterise these changes in as much detail as possible.
Through new research published in EPJ B, researchers led by Vera Pecorino at the University of Catania, Italy, present a highly detailed analysis of recent changes in seasonal rainfall on the Italian island of Sicily. Their results confirm that over the past decade, the island’s rainfall patterns underwent a profound shift from a 4- to a 2-season cycle.
EPJ ST Highlight - Modelling Brain Networks in Parkinson’s Disease
- Details
- Published on 18 November 2024

Insights from network theory have led to a novel mathematical representation of Parkinson’s disease development with potential clinical applications
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, can be thought of as arising from malfunctions in the network of neuronal agglomerates in the brain. It is therefore often useful to apply insights from a branch of mathematics called network theory when studying the development of these diseases. A group of European physicists and engineers led by Maria Mannone of the National Research Council of Italy, the University of Potsdam, Germany, and the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), Germany, has now taken this further by defining a matrix transforming the brain network of a healthy individual into one affected by Parkinson’s disease. This has now been published in EPJ Special Topics (EPJ ST).
EPJ ST Highlight - A mathematical approach to simulating electromagnetic field of ReBCO superconductors
- Details
- Published on 15 November 2024

Electromagnetic field and alternating current loss in high-temperature ReBCO superconductors can be obtained by treating their complex electromagnetic interactions as a convex optimisation problem
Rare-earth barium copper oxides (ReBCO) are a family of superconducting materials that allow electrical currents to flow with zero resistance, even at temperatures well above absolute zero. This allows them to sustain stronger magnetic fields than other type of superconductors. However, these materials often host a complex nonlinear electromagnetic response. So far, it is a challenge to deal with the electromagnetic problem of ReBCO superconductors accurately and efficiently.
Through new research published in EPJ Special Topics (EPJ ST), Huadong Yong and colleagues at Lanzhou University, China, show that the electromagnetic problem with power law relation can be approached as a mathematical challenge known as a ‘convex optimisation problem’. By applying this problem-solving method, the team was able to accurately calculate the electromagnetic field and alternating current loss for a variety of real-life superconducting structures.
EPJ E Highlight - Macroscopic and microscopic structures of clay-surfactant mixtures
- Details
- Published on 28 October 2024
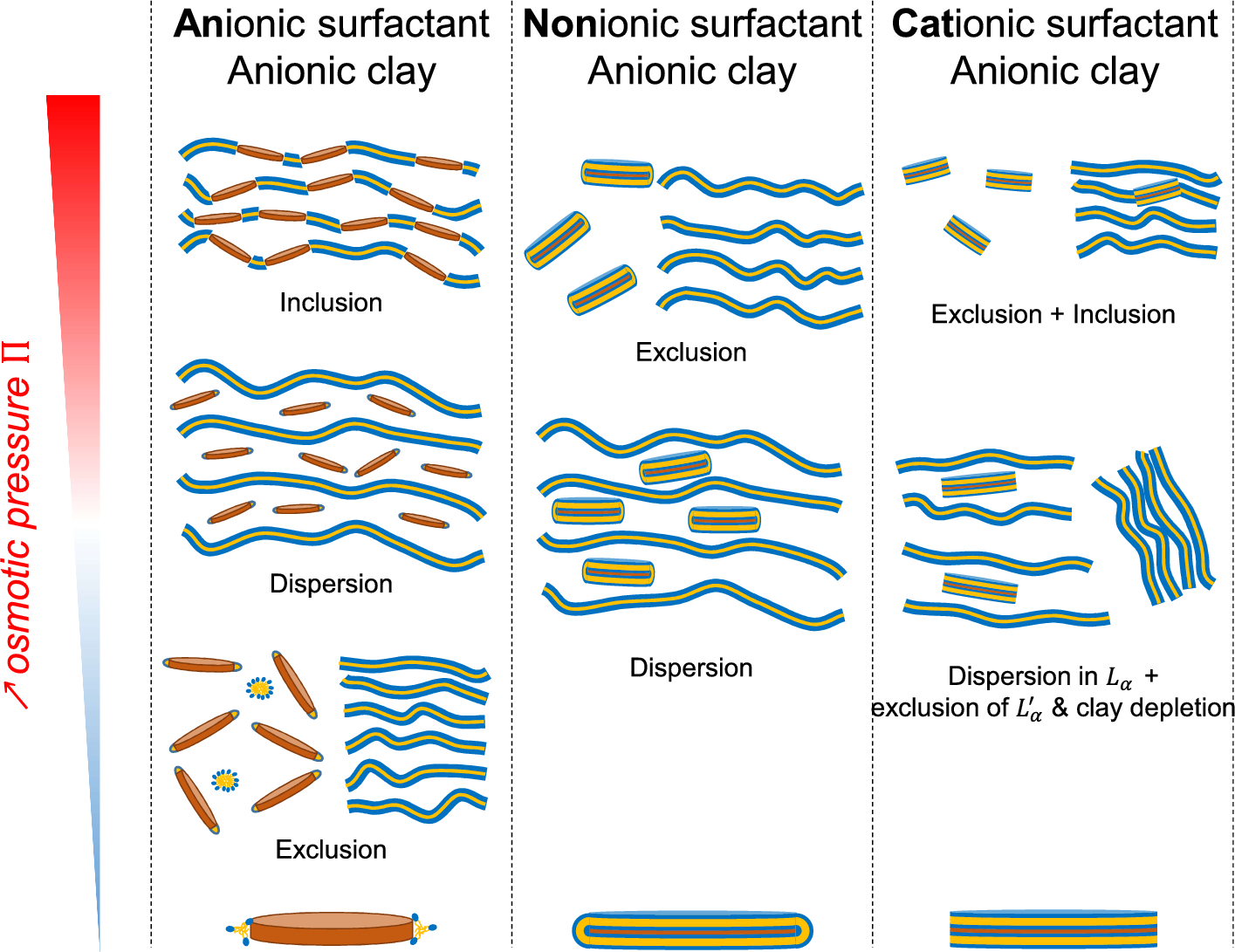
As a tribute to the late colloid scientist Isabelle Grillo, two of her principal co-workers have published a summary of some of the ground-breaking work in her PhD thesis.
The premature death of Isabelle Grillo (1972-2019), a distinguished colloid scientist at the Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL), Grenoble, France, left much of the work on clay-surfactant mixtures that she had presented in her PhD thesis still unpublished. This gap has now been filled by two of her former co-workers, Sylvain Prévost of ILL and Thomas Zemb of the Institut de Chimie Separative de Marcoule, Bagnols-sur-Cèze, who have published an extensive overview of this work and her legacy in EPJ E.
EPJ E Highlight - Investigating the Flow of Fluids with Non-Monotonic, ‘S-shaped’ Rheology
- Details
- Published on 28 October 2024
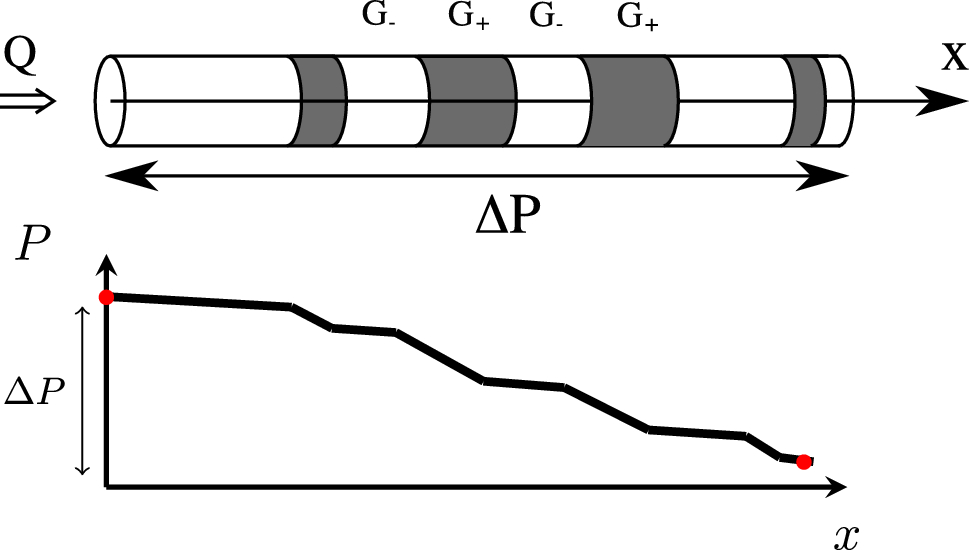
Analysis of cornstarch suspensions under different stresses suggests that some fluids with non-monotonic rheology can segregate into regions of high and low viscosity in a capillary tube.
Water and oil, and some other simple fluids, respond in the same way to all levels of shear stress and, as termed Newtonian fluids, their viscosity is constant for all stresses although it will vary with temperature. Other non-Newtonian fluids exhibit much more complex patterns of behaviour under different stresses and pressure gradients. Laurent Talon and Dominique Salin from Université Paris-Sacly, Paris, France have now shown that, under certain circumstances, cornstarch suspensions can display a banding pattern with alternating regions of high and low viscosity. This work has been published in the journal EPJ E.
EPJ C: Susha Parameswaran appointed Guest Editor for String Phenomenology
- Details
- Published on 18 October 2024

EPJ C is pleased to announce the appointment of Susha Parameswaran as the journal’s Guest Editor for String Phenomenology. Susha Parameswaran is a theoretical physicist based in the UK at the University of Liverpool.
Her research interests are in string theory and its applications and potential implications across particle physics and cosmology.
Together with Ignatios Antoniadis, Associate Editor of EPJC, she will supervise the long-term topical collection which has now opened for submissions:
String theory predictions for astroparticle and collider physics, and beyond




